Exploring the Different Strategies and Solutions for Effective Damp Proofing
Wetness in buildings postures considerable obstacles to both architectural integrity and indoor air high quality. Different methods and solutions have actually arised to battle this prevalent concern. From traditional damp-proof membranes to innovative chemical therapies, each method offers distinct advantages. Understanding these options is vital for reliable dampness control. Picking the ideal option depends on certain building conditions and needs, motivating more exploration into the most effective wet proofing methods offered.
Recognizing the Sources Of Dampness
Wetness can occur from numerous sources, recognizing these reasons is crucial for efficient remediation. Generally, moisture stems from three primary sources: rising moist, penetrating moist, and condensation. Rising moist occurs when groundwater takes a trip up with porous products, such as block or rock, frequently as a result of an absence of an effective obstacle (damp removal newcastle). Permeating damp is generally created by exterior aspects, including roofing leakages, malfunctioning gutters, or damaged wall surfaces, allowing water to infiltrate a residential or commercial property. Condensation, on the various other hand, results from excess wetness airborne, usually intensified by inadequate ventilation and temperature distinctions, bring about water beads basing on surfaces. Recognizing these underlying issues is important, as each kind of wetness requires a tailored approach for removal. Appropriate analysis assists in identifying the most efficient options, eventually securing the architectural stability of a structure and boosting interior air top quality
Traditional Damp-Proof Membranes
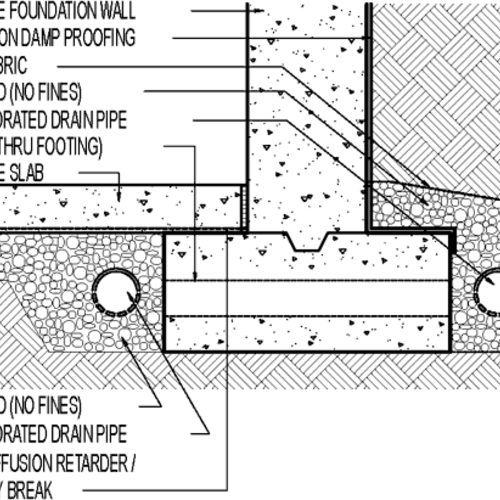
Chemical Damp-Proofing Solutions
Chemical damp-proofing services provide an ingenious method to stop wetness invasion in buildings. These methods usually include the application of liquid chemicals that penetrate stonework and create an obstacle versus climbing wet. Generally used chemicals consist of silanes, siloxanes, and other water-repellent representatives that respond with surface materials to develop a hydrophobic layer.The application procedure typically calls for boring holes into the wall surfaces, injecting the chemical service, and allowing it to heal. This technique is especially advantageous for older structures where conventional damp-proof membranes may be impractical. Chemical damp-proofing can be less turbulent and a lot more economical than extensive improvement projects.While efficient, these services depend on correct application and environmental conditions for peak efficiency. damp specialist newcastle. Routine maintenance and tracking are vital to guarantee the durability of the damp-proofing treatment. Overall, chemical damp-proofing stands for a versatile alternative for safeguarding buildings against moisture-related damages
Dental Caries Wall Surface Construction Methods
Tooth cavity wall surface building strategies provide numerous advantages, particularly in dampness control and energy efficiency. By integrating an air void between two layers of stonework, these wall surfaces effectively reduce water access while boosting insulation. This mix not just shields structures from dampness yet additionally adds to lowered energy consumption.
Advantages of Cavity Walls
When thinking about reliable wet proofing approaches, the benefits of cavity walls attract attention plainly. Cavity wall surfaces contain 2 separate layers, creating an air gap that properly reduces moisture penetration. This design minimizes the risk of wetness, as the external wall surface works as an obstacle versus rainfall and water access. In addition, tooth cavity wall surfaces improve thermal insulation, which contributes to energy efficiency by lowering warmth loss. They also provide audio insulation, assisting to produce a quieter indoor environment. The air gap allows for ventilation, which aids in dampness control and lowers the chance of mold and mildew growth. These advantages not only improve the total convenience of a building but likewise add to its long life and architectural stability.
Moisture Control Approaches
Effective dampness control techniques are critical in tooth cavity wall surface construction to ensure long-term security versus moisture. One primary technique entails the consolidation of weep openings, which assist in water drain from the tooth cavity, avoiding buildup. Additionally, the use of breathable membrane layers can help take care of moisture levels while permitting trapped vapor to get away. Correct placement of insulation is additionally important, as it should not block drainage courses. Guaranteeing that the external fallen leaves of the cavity wall surface are built with waterproof materials enhances total durability. Routine upkeep checks are necessary to identify any kind of clogs or damage early, guarding the framework's stability. Ultimately, a combination of these methods develops a robust defense against moisture breach in cavity wall surfaces.
Insulation and Power Effectiveness
Insulation plays a crucial duty in boosting power performance within cavity wall construction. By including insulating products, these walls develop a thermal obstacle that minimizes warmth loss and lowers power usage. Effective insulation not just aids preserve a stable indoor temperature yet also reduces the risk of wetness, as it stops condensation within the wall cavity. Numerous methods, such as using stiff foam boards or mineral woollen, can be employed to attain ideal insulation efficiency. Furthermore, proper installment is essential to ensure that voids read more and gaps are decreased, which can otherwise endanger energy performance. Inevitably, a well-insulated cavity wall surface contributes greatly to general sustainability and decreases heating & cooling prices for house owners.
Exterior Damp Proofing Approaches
Outside moist proofing methods are necessary for safeguarding structures from moisture infiltration. 2 effective methods consist of the application of waterproof membranes and the setup of French drains. These remedies assist mitigate water build-up and preserve the stability of structures.
Waterproof Membrane Layer Application
While different techniques exist for avoiding dampness ingress, the application of water-proof membrane layers remains an extremely reliable external moist proofing method. These membrane layers are normally made from materials such as polyethylene, rubber, or customized asphalt, giving a durable obstacle against water infiltration. The installation process entails using the membrane to the outside surfaces of walls or structures, making sure total coverage to stop leakages. Correct bond and sealing at joints are critical to taking full advantage of performance. Water-proof membranes can be applied in different types, consisting of fluid layers and sheet membrane layers, permitting flexibility based on the particular needs of the framework. This approach not only shields buildings from dampness but additionally boosts their long life and architectural stability.
French Drain Installation
One effective approach for handling groundwater and stopping wetness accumulation around a structure's structure is the setup of a French drain. This water drainage system is composed of a trench filled up with gravel and a perforated pipe that reroutes surface area water far from the structure. Appropriate setup needs cautious preparation, guaranteeing that the drain slopes away from the structure to help with suitable water circulation. Additionally, the location of the drain is essential; it must be placed in areas prone to pooling or excess dampness. Routine maintenance, consisting of clearing particles from the gravel and ensuring the pipeline remains unhampered, is necessary for long-term performance. Ultimately, a well-installed French drain can considerably decrease the threat of water-related problems in basements and structures.
Interior Waterproofing Methods
Inside waterproofing techniques are essential for shielding a building's inside from dampness infiltration and possible water damages. These techniques commonly include the application of customized products and techniques created to develop a moisture barrier within the framework. One usual method is using waterproof finishings or sealers on walls and floors, which protect against moisture from permeating surfaces.Additionally, mounting interior drain systems, such as sump pumps, can properly manage water build-up in cellars and creep areas. An additional method includes using vapor barriers, which are mounted to prevent moisture movement from the ground into living spaces.Moreover, attending to any cracks or spaces in wall surfaces or foundations with ideal sealers ensures a comprehensive protection against water invasion. By executing these interior waterproofing approaches, residential or commercial property owners can considerably lower the threat of mold development, architectural damage, and various other moisture-related problems. Proper implementation of these methods is necessary for long-lasting protection and structure stability.
Routine Upkeep and Examination Practices
Routine maintenance and evaluation methods are crucial for guaranteeing the long-term performance of damp proofing remedies in any kind of structure. Routine checks enable homeowner to determine early indicators of moisture intrusion, such as peeling off paint, mold growth, and mildewy smells. These signs can indicate underlying problems that call for immediate attention.Inspections need to be carried out at least annually, concentrating on at risk locations like basements, creep rooms, and exterior wall surfaces. Throughout these evaluations, homeowner need to check out sealants, drain systems, and air flow to validate they work correctly.Additionally, keeping seamless gutters and downspouts is important, as clogged up systems can lead to water accumulation near the structure. Carrying out a normal upkeep routine, along with prompt repairs, can considerably prolong the life expectancy of wet proofing measures and shield the architectural integrity of the building. Aggressive measures eventually add to the total wellness and safety of the living environment.
Often Asked Concerns
How Much Time Does Damp Proofing Usually Last?
The period of wet proofing efficiency varies, generally lasting in between 20 to 50 years. Aspects such as application quality, environmental conditions, and maintenance methods substantially affect the durability of the damp proofing treatment.

Can I Damp Evidence My Home Myself?
The specific contemplated the feasibility of DIY damp proofing. With correct research and the right materials, it is feasible. However, they also identified the relevance of expert guidance to assure durable efficiency and stop future concerns.
What Are the Indications of Inefficient Damp Proofing?
Indications of inefficient damp proofing include relentless mildewy odors, visible mold growth, peeling off paint, damp patches on walls, and wood decay - damp specialist newcastle. Home owners ought to attend to these concerns quickly to avoid more damage and wellness concerns
Does Damp Proofing Affect Indoor Air High Quality?

Just How Much Does Expert Damp Proofing Cost?
Expert damp proofing expenses differ substantially, usually varying from $1,000 to $5,000 relying on the property's size, the level of the damp concern, and chosen techniques. Each circumstance needs a customized assessment for accurate rates. Generally, dampness stems from three main resources: rising damp, penetrating damp, and condensation. When taking into consideration reliable moist proofing methods, the advantages of cavity walls stand out plainly. Exterior moist proofing techniques are necessary for securing structures from wetness seepage. While various techniques exist for preventing wetness ingress, the application of water resistant membranes continues to be a very effective exterior wet proofing method. Indicators of inefficient moist proofing consist of persistent mildewy smells, noticeable mold growth, peeling off paint, wet patches on wall surfaces, and timber degeneration.